- Home
- Corporate
- GENITAL AESTHETICS
- GYNECOLOGICAL LASER
-
GYNECOLOGY
- Urinary Incontinence Treatment
- Vaginismus Treatment
- Laparoscopic Surgeries
- Cervical Cancer Tests
- Genital Warts
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
- Menopause Period
- Cervical Wounds
- Infertility
- Chocolate Cyst
- Benign Uterine Tumors
- HPV DNA Test
- HPV Vaccines
- Family Planning
- Urinary Incontinence Tot Surgery
- Smear Test
- Intrauterine Biopsy
- Vaginal Ultrasonography
- Blog
- Contact
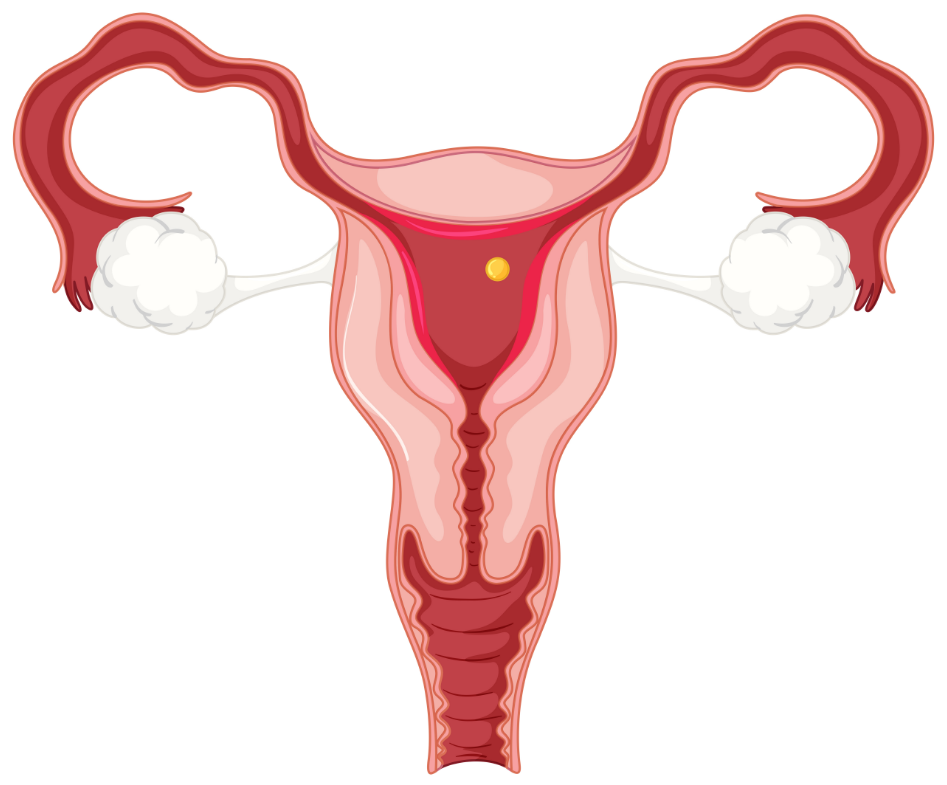
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Although the exact cause is not known, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, which occurs as a result of different risk factors such as genetic factors, environmental factors or increased insulin secretion; It is a hormonal disorder that can cause irregular menstrual periods, hair loss in different parts of the body, hair loss, weight problems and infertility in women in the reproductive period.
Due to imbalances in estrogen and progesterone hormones, women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome have irregularities in egg development and release. Therefore, the risk of infertility increases, quality of life deteriorates, and mostly thickening of the outer walls of the ovaries and cyst formation occur in the region.
What are the Symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
The symptoms and severity of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome can vary from person to person. The most common symptoms of this hormonal disorder can be listed as follows:
Menstrual irregularities; Menstrual irregularities occur in PCOS patients. In some women, the menstrual cycle drops below 21 days, while in some women the menstrual cycle is interrupted. Disruption in the menstrual cycle causes the ovulation cycle to change and therefore the probability of pregnancy to occur decreases.
PCOS; It causes hair growth on the face, chin and different parts of the body in women. Hair growth problem is seen in 70% of women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
polycystic ovary syndrome; It can cause deterioration in the skin of women and can also cause male pattern baldness in women.
Difficulty in gaining or losing weight is a common feature of PCOS patients.
What are the Causes of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
Although the causes of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome are not fully known, it is accepted that there are various risk factors that can lead to this disease. Genetic factors, diseases that cause changes in hormone levels, nutritional mistakes and obesity are among the factors that trigger the formation of PCOS.
How is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Diagnosed?
For the diagnosis of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, the patient's history is listened; The diagnosis is made by evaluating the data obtained as a result of clinical findings, laboratory tests and ultrasound examination. During the physical examination, Body Mass Index and waist circumference are measured, skin control is performed and whether there is hair loss is investigated. Within the scope of pelvic examination, the ovaries are checked and a pelvic ultrasound called sonogram is taken. After blood tests are done to determine the level of androgen hormone, the treatment process is shaped.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Treatment
Treatment methods to be applied within the scope of PCOS treatment are determined individually for the patient. Although there is no standard treatment method; lifestyle changes, medications that increase insulin sensitivity, or use of birth control pills to regulate menstrual periods may be necessary. Surgical treatment can be recommended for patients whose cyst problem persists after follow-up and drug treatments.

 TR
TR
 EN
EN
 DE
DE
 AR
AR