Benign Uterine Tumors
Uterine lumps, also called fibroids or fibroids; It can be defined as benign, that is, non-cancerous growths. Fibroids, which occur in approximately 30% of all women, often do not cause obvious symptoms. In some women, due to their location, number and size, they may cause complaints such as menstrual pain, vaginal bleeding, anemia, irregularity and pain in menstrual periods.
What are the Causes of Myoma?
Although fibroids are benign tumors in the uterus that are frequently seen and can reduce the life comfort of women, the reasons for their formation are not yet known clearly. However, as a result of scientific studies;
Estrogen and progesterone hormones
obesity disease,
genetic factors and
Hormonal changes during pregnancy have been shown to trigger myoma formation.
What Are the Symptoms of Myoma?
Myoma symptoms may vary depending on the patient's number of cysts, the location and size of the cysts. If benign uterine tumors are very small and a woman is close to menopause, she may not experience any symptoms. The decrease in estrogen and progesterone levels after menopause causes tumors to shrink.
Symptoms such as severe bleeding during or between menstrual periods, pain in the pelvic region, menstrual pain, pain during sexual intercourse, prolonged menstrual periods, swelling in the abdomen can also be among the symptoms of fibroids.
How Are Benign Uterine Tumors Diagnosed?
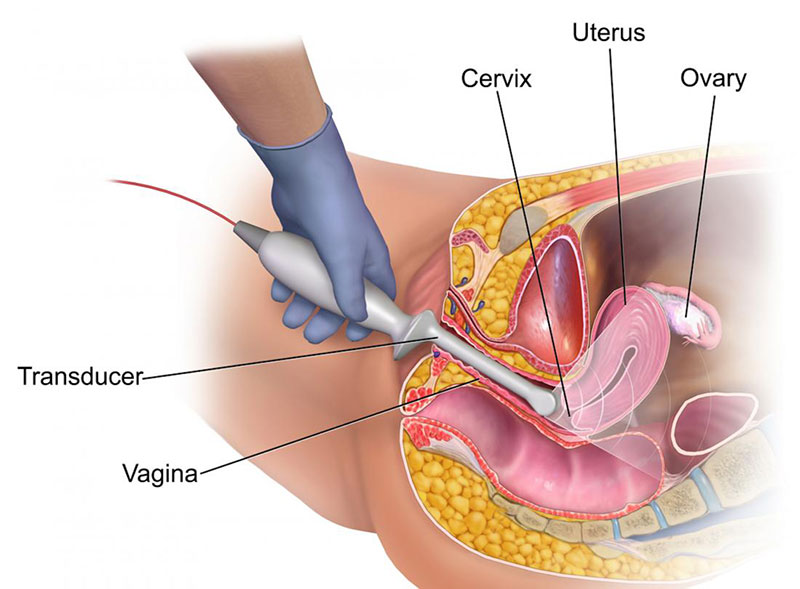
For the diagnosis of benign uterine tumors, a gynecological examination should be performed. In this process, the vagina, cervix, vulva, fallopian tubes, uterus and ovaries are thoroughly examined. In addition to gynecological examination, imaging methods such as pelvic MRI, ultrasound and transvaginal ultrasound can also be used for fibroid diagnosis.
Treatment of Benign Uterine Tumors
As we just mentioned, not every fibroid can be treated. At this point, dynamics such as the patient's complaints, age, whether there was a previous pregnancy loss, and the continuity of the desire to reproduce are important.
The first-stage treatment of fibroids is done with drugs. If it is not possible to shrink the fibroids and reduce the complaints of the patients with drugs, surgical operations can be applied for the treatment of fibroids. Within the scope of the surgical operation to be preferred, the preferences of the patient and the characteristics of the patient are decisive.
If very large fibroids need to be removed and the patient does not want to have children, fallopian tubes, ovaries and uterus can be removed by hysterectomy operation. Myomectomy surgery can be performed on women who are planning to have children. However, myomectomy may not be the solution for women who have very large fibroids or those whose fibroids are located in parts of the uterus. In addition to myomectomy and hysterectomy, methods such as endometrial ablation or embolization of uterine fibroids can also be applied within the scope of myoma treatment.



 Türkçe
Türkçe  English
English  Deutsch
Deutsch  فارسی
فارسی